How To Set Up a Firewall Using firewalld on CentOS/RHEL 8
Firewalld is a powerful and simple to use tool to manage a firewall on CentOS/RHEL 8 Server. By default, few services to receive incoming traffic are enabled. You can set up rules to either block or allow traffic. In CentOS/RHEL 8 nftables replaces iptables as the default Linux network packet filtering framework.

Useful Articles:
- LINUX FIREWALL – BASIC GUIDE OF IPTABLES
- BLOCK COUNTRIES USING CSF FIREWALL ON LINUX
- USE OF CSF FIREWALL IN LINUX
- WHAT IS FIREWALLD AND IT’S PREDEFINED ZONES
- INSTALL CSF (CONFIGSERVER FIREWALL) ON LINUX
- HOW TO INSTALL PROFTPD SERVER ON RHEL/CENTOS 7
In this article, we will explain how To Set Up a Firewall Using firewalld on CentOS/RHEL 8
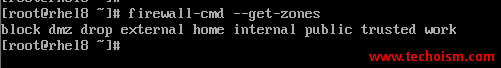
Zones
Each zone can be configured to allow or deny services/ports. The zone can be associated with one or more network interfaces.
# firewall-cmd --get-zones
block dmz drop external home internal public trusted work
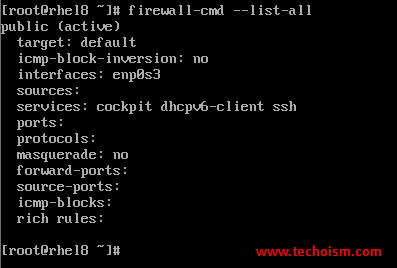
List all the open ports and services using the mentioned command.
# firewall-cmd --list-all
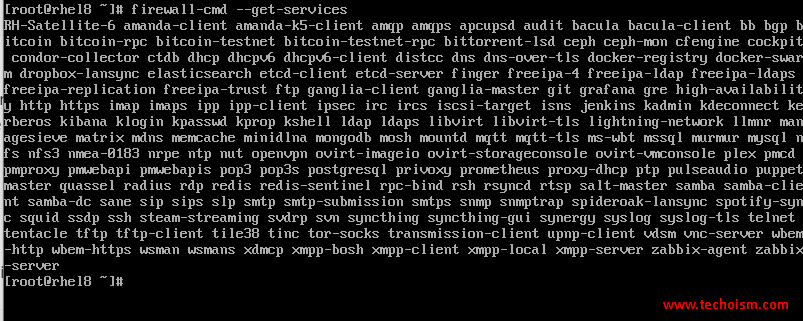
You can see which services are allowed in the current zone.
# firewall-cmd --get-services
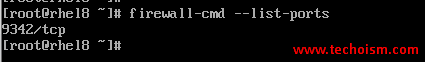
You can see which ports are allowed in the current zone.
# firewall-cmd --list-ports
List firewall rules for ports or services associated with the any specific zone
# firewall-cmd --list-all --zone=Zone_Name
For Eg:
# firewall-cmd --list-all --zone=public # firewall-cmd --list-all --zone=dmz # firewall-cmd --list-all --zone=drop
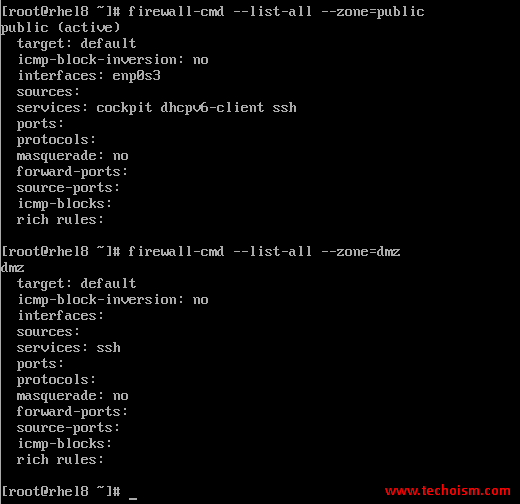
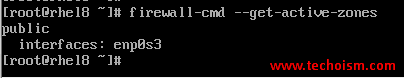
We can verify the active zone using the following command.
# firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
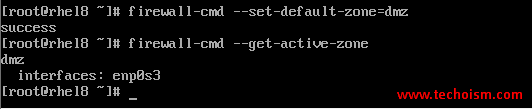
You can change the default zone also. Use the mentioned command to change the zone.
# firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=dmz
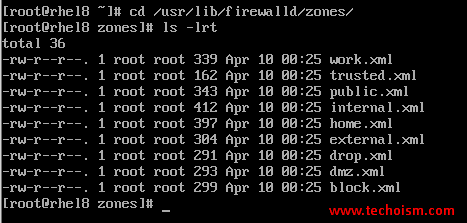
You can see all zone files at the below location.
# ls -l /usr/lib/firewalld/zones/
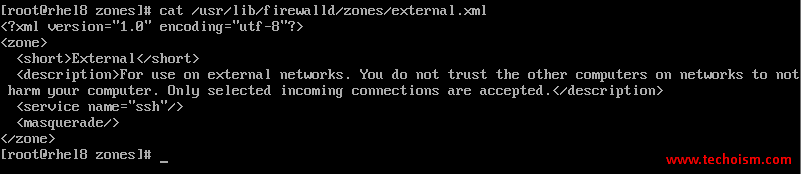
Use the cat command to view the external zone:
# cat /usr/lib/firewalld/zones/external.xml
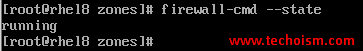
Check the firewalld status.
# firewall-cmd --state
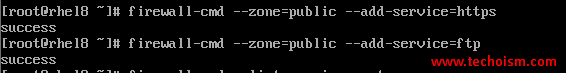
Configure Firewalld Temporary
You need to configure the firewall rules to the default zone so that your service will be accessible based on your requirement. But below changes will be temporary, When you reboot the server, changes will go.
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=https # firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=ftp
In case you want to open a port temporary which is not a part of the preconfigured services then use the mentioned command.
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=9342/tcp
Note: In place of DMZ you can mention the zone in which you want to configure the firewall rule.
Configure Firewalld Permanently
You can configure the firewall rules permanently also so that after the server reboot also changes will exist.
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http --permanent # firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=dhcp --permanent # firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=smtp --permanent
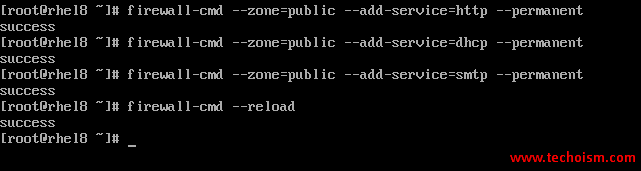
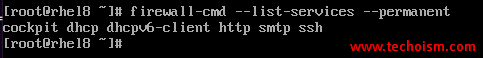
Verify it:
# firewall-cmd --list-services --permanent
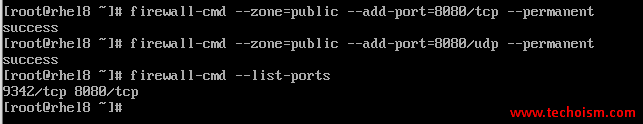
In case you want to open a port permanently which is not a part of the preconfigured services then use the mentioned command.
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent # firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8080/udp --permanent
Verify it:
# firewall-cmd --list-ports --permanent
If you need to configure the firewall rules to any other zone so use the following command.
# firewall-cmd --zone=dmz --add-service=https
Note: In place of DMZ you can mention the zone in which you want to configure the firewall rule.
Reload firewall settings. Once you have opened the port or services make sure to reload the firewall:
# firewall-cmd --reload
Remove Firewalld Rules
In case you wish to close a specific port or service use the below command to remove the firewall rules.
## For Port ##
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --remove-port 8080
## For Service ##
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --remove-service dhcp
Reference:
- https://firewalld.org/
- https://firewalld.org/documentation/
Enjoy it!
