How to configure Master-Slave MySQL Replication on CentOS/RHEL 5/6/7
By Anuket Jain On 9 August 2015 In Database
MySQL replication is a procedure that permits you to easily keep up multiple copies of a MySQL data by having them replicated consequently from an master to a slave database. This can helpful for some reasons including facilitating a backup for the data, a way to analyze it without utilizing the main database.
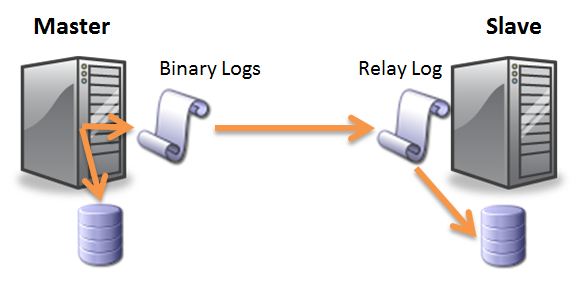
MySQL replication for the most part comprises of three-section process:
- The master server records all data changes to its binary logs and send it to the slave using a thread called Binlog dump thread once the slave connects to the master.
- The slave copies the binary log events sent by the master’s binlog dump thread to its relay logs using a thread called Slave I/O thread.
- The slave applies these changes from the relay logs to its data by replaying (executing) all events using a thread called Slave SQL thread.
Server Details:
Master Server: 192.168.10.4
Slave Server: 192.168.10.50
Database Name: techoism
Basic Configuration:
- Install below repository on Master and Slave server:
# rpm -Uvh http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm # rpm -Uvh http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/remi-release-6.rpm
- Disabled selinux from Master and Slave server (If it is in Enforcing or Permissive mode)
# vim /etc/selinux/config OR # vim /etc/sysconfig/selinux
SELINUX=disabled
- After disabled the selinux reboot both the server.
- Comment old_passwords line from both database server (If It is not commented)
# vim /etc/my.cnf
# old_passwords=1
- Restart MySQL from both server so that configuration changes take place:
For CentOS/RHEL 5/6: # /etc/init.d/mysql restart For CentOS/RHEL 7: # systemctl restart mysqld
- Install php mysql module using below command:
# yum install php-mysql --enablerepo=remi
- Restart Apache Service from both server so that changes will reflect:
For CentOS/RHEL 5/6: # /etc/init.d/httpd restart For CentOS/RHEL 7: # systemctl restart httpd
Master Server Configuration:
- Create new mysql user and provide Grant privileges to that user to access the database.
mysql> CREATE USER 'new_user'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'secretpassword'; mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON techoism.* TO 'username'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION; mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES
- Check mysql connectivity with Slave server
# telnet slave_server_ip 3306
- Start iptables service (if connectivity with server will fail)
For CentOS/RHEL 5/6 # /etc/init.d/iptables stop For CentOS/RHEL 7 # systemctl stop firewalld
- Add the following variables to the MySQL configuration file
# vim /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld] log-bin=mysql-bin binlog-do-db=techoism server-id=1 innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=1 sync_binlog=1
- Run below command to configure replication:
mysql>GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON techoism.* TO 'new_user'@'192.168.10.50' IDENTIFIED BY 'secretpassword'; mysql>FLUSH PRIVILEGES; mysql> use techoism; mysql> FLUSH TABLES WITH READ LOCK; mysql> exit;
- Restart MySQL so that configuration changes take place:
For CentOS/RHEL 5/6: # /etc/init.d/mysql restart For CentOS/RHEL 7: # systemctl restart mysqld
- Check Master Status using following command.
mysql> SHOW MASTER STATUS\G
+------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | mysql-bin.000002 | 107 | techoism | | +------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+
- Take a full backup from the master’s database:
# mysqldump -u username -p techoism > techoism.sql
Note: If we want to take dump without triggers then use below command
# mysqldump -u username -p --skip-triggers techoism > techoism.sql
- Unlock database tables:
mysql> UNLOCK TABLES;
- Copy database on slave
# scp techoism.sql root@slave_server_ip:/home/
Slave Server Configuration:
- Check connectivity with master server
# telnet server_ip 3306
- Start iptables service (if connectivity with server will fail)
For CentOS/RHEL 5/6 # /etc/init.d/iptables stop For CentOS/RHEL 7 # systemctl stop firewalld
- Add the following variables to the MySQL Configuration file:
# vim /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld] server-id=2 replicate-do-db=techoism
- Restart Mysql Service
For CentOS/RHEL 5/6 # /etc/init.d/mysqld restart For CentOS/RHEL 7 # systemctl restart mysqld
- Create new database and restore database using below steps:
# mysql -u root -p -e "create database techoism" # cd /home # mysql -u root -p techoism < techoism.sql
- Run below command to configure replication
# CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='192.166.10.4', >MASTER_USER='repl_50', >MASTER_PASSWORD='secretpassword', >MASTER_LOG_FILE='mysql-bin.000002', >MASTER_LOG_POS=107;
- Start Slave
mysql> SLAVE START;
- Check status of slave
mysql> show slave status\G
*************************** 1. row *************************** Slave_IO_State: Master_Host: 192.168.1.150 Master_User: new_user Master_Port: 3306 Connect_Retry: 60 Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000002 Read_Master_Log_Pos: 107 Relay_Log_File: mysqld-relay-bin.000001 Relay_Log_Pos: 4 Relay_Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000002 Slave_IO_Running: No Slave_SQL_Running: No Replicate_Do_DB: techoism Replicate_Ignore_DB: Replicate_Do_Table: Replicate_Ignore_Table: Replicate_Wild_Do_Table: Replicate_Wild_Ignore_Table: Last_Errno: 0 Last_Error: Skip_Counter: 0 Exec_Master_Log_Pos: 107 Relay_Log_Space: 107 Until_Condition: None Until_Log_File: Until_Log_Pos: 0 Master_SSL_Allowed: No Master_SSL_CA_File: Master_SSL_CA_Path: Master_SSL_Cert: Master_SSL_Cipher: Master_SSL_Key: Seconds_Behind_Master: NULL Master_SSL_Verify_Server_Cert: No Last_IO_Errno: 0 Last_IO_Error: Last_SQL_Errno: 0 Last_SQL_Error: Replicate_Ignore_Server_Ids: Master_Server_Id: 1 1 row in set (0.00 sec) # mysql>
No Responses