What is Docker & Docker Container ?
What is Docker & Docker Container
Docker is an open-source software platform to create, deploy and manage virtualized application containers on a common operating system. Docker enables developers to run any application as a lightweight, which can run virtually anywhere. It also ensures that there is process level isolation, meaning each application is independent of other applications, giving developers surety that they can build applications that will not interfere with one another.
A Docker container packages the application service or function with all of the libraries, configuration files, dependencies and other necessary parts to operate. Each container shares the services of one underlying operating system. Containers do this by enabling developers to isolate code into a single container. This makes it easier to modify and update the program.
Useful Articles:
- HOW TO INSTALL DOCKER ENGINE ON UBUNTU 19.10/18.04
- HOW TO INSTALL DOCKER ENGINE ON CENTOS/RHEL 8
- HOW TO INSTALL DOCKER ON UBUNTU 18.04 & 16.04 LTS
- WHAT IS DOCKERFILE AND BASICS OF DOCKERFILE
- HOW TO INSTALL DOCKER CE ON CENTOS/RHEL 7/6
- INSTALLATION OF DOCKER FAILS ON CENTOS 8 WITH ERROR – PACKAGE CONTAINERD.IO-1.2.10-3.2.EL7.X86_64 IS EXCLUDED
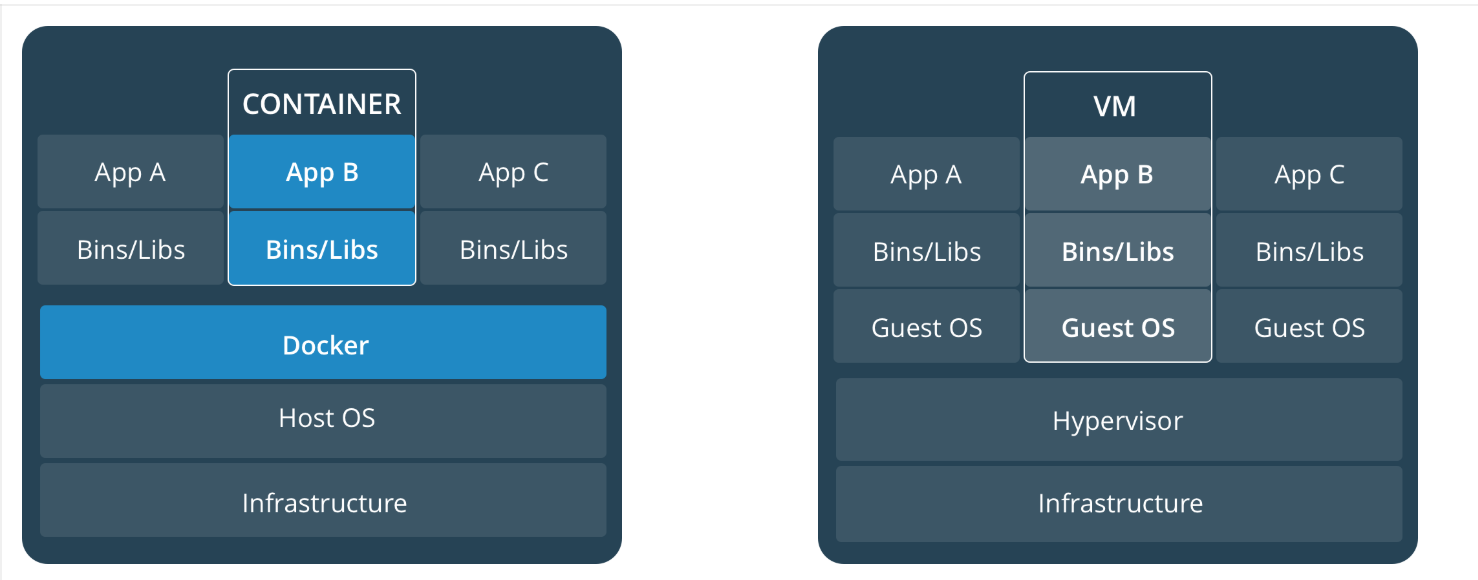
Docker VS Virtual Machine (VM)
- The container gives a number of advantages over VMs. One preferred advantage is the low overhead of containers and in this way the ability to begin new containers quickly. VM time, memory and the space required for the VM disk storage.
- Docker is container-based technology and containers are simply use space of the operating system. At a low level, a container is just a set of processes that are isolated from the rest of the system. On another hand under a virtual machine, the server hardware is virtualized. Each VM has an Operating system (OS) & apps. It shares a hardware resource from the host.
- Docket and VM begin with some type of infrastructure. This could be your laptop, a dedicated server running in a data center, or a virtual private server that you’re using in the cloud.
- Docker containers are suited for circumstances where you want to run many applications over a single OS kernel. But if you have applications or services that need to keep running on various OS flavours, VMs are required.
- In Docker, since the host kernel is shared among the containers, the container technology has access to the kernel subsystems. Accordingly, a single unsafe application can hack the complete host server. Then again, VMs are unique instances with their own kernel and security features. They can, accordingly, run applications that need more privilege and security.
- Docker and Virtual machines are designed for different purposes, so it’s not fair to measure their performance equally. But their light-weight architecture makes Docker containers less resource-intensive than the virtual machines.
- In containers, the resource usage such as CPU, memory, I/O, etc. changes with the load or traffic in it. Unlike the case of VMs, there is no need to allocate resources permanently to containers.
- Scaling up and increasing the containers is also an easy task compared to that of VMs, as there is no necessity to install an operating system in them.
Enjoy it!