Cloud Computing Introduction
Cloud computing is a type of computing that relies on sharing computing resources rather than having local servers or personal devices to handle applications. In the simplest terms, cloud computing means storing and accessing data and programs over the Internet instead of your computer’s hard drive.

Advantages of Cloud Computing:
Pay per use:
Computing resources are measured at a granular level, allowing users to pay only for the resources and workloads they use.
Flexible and Scalable:
Since virtual servers aren’t physical, they are super flexible, giving you what you need at the moment. Spin up a server in minutes, and take it down just as easily.
Resiliency and Redundancy:
One of the benefits of a private cloud deployment is that you can get automatic failover between hardware platforms and disaster recovery services to bring up your server set in a separate data center should your primary data center experience an outage.
Always-on availability:
Most cloud providers are extremely reliable in providing their services, with many maintaining 99.99% uptime.
Expenses can be quickly reduced:
During times of recession or business cut-backs, cloud computing offers a flexible cost structure, thereby limiting exposure.
Elasticity:
Companies can scale up as computing needs increase and then scale down again as demands decrease.
Backup and Recovery:
Since all your data is stored in the cloud, backing it up and restoring the same is relatively much easier than storing the same on a physical device.
Easy Access to Information:
Once you register yourself in the cloud, you can access the information from anywhere, where there is an Internet connection.
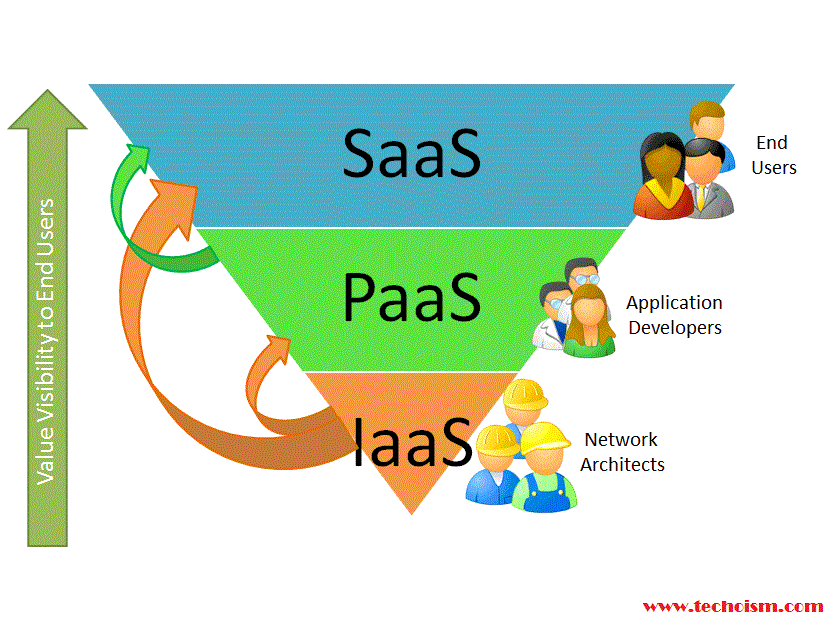
Cloud Stack
1. Software as a Service(SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) makes use of a cloud computing infrastructure to deliver one application to many users, regardless of their location, rather than the traditional model of one application per desktop. It allows activities to be managed from central locations in a one-to-many model, including architecture, pricing, partnering, and management characteristics.
Benefits:
Some defining characteristics of SaaS include:
- No additional hardware costs
- No initial setup costs
- Pay for what you use
- Usage is scalable
- Updates are automated
- Accessible from any location
- Users not required to handle software upgrades and patches
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a category of cloud computing that provides a platform and environment to allow developers to build applications and services over the internet. PaaS services are hosted in the cloud and accessed by users simply via their web browser.Benefits:
Some defining characteristics of PaaS include:
- They don’t have to invest in physical infrastructure
- Makes development possible for ‘non-experts
- Develop applications and get to market faster
- Deploy new web applications to the cloud in minutes
- Teams in various locations can work together
- Reduce complexity with middleware as a service
3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
In an IaaS model, a third-party provider hosts hardware, software, servers, storage and other infrastructure components on behalf of its users. IaaS providers also host users’ applications and handle tasks including system maintenance, backup and resiliency planning.IaaS platforms offer highly scalable resources that can be adjusted on-demand. This makes IaaS well-suited for workloads that are temporary, experimental or change unexpectedly.Benefits:
Some defining characteristics of IaaS include:
- Resources are distributed as a service
- Allows for dynamic scaling
- Has a variable cost, utility pricing model
- Generally includes multiple users on a single piece of hardware
Enjoy it!